Tecam RCO
Regenerative
CATALYTIC Oxidation
Tecam’s RCO systems
Tecam’s RCO systems are designed to work at temperatures ranging from 250 ºC – 350 ºC. The fact that the system is regenerative, combined with the low temperature at which catalytic oxidation takes place, makes it extremely energy efficient for production processes with a medium or low load of VOCs, resulting in an optimal combination of thermal efficiency and VOC oxidation efficiency.
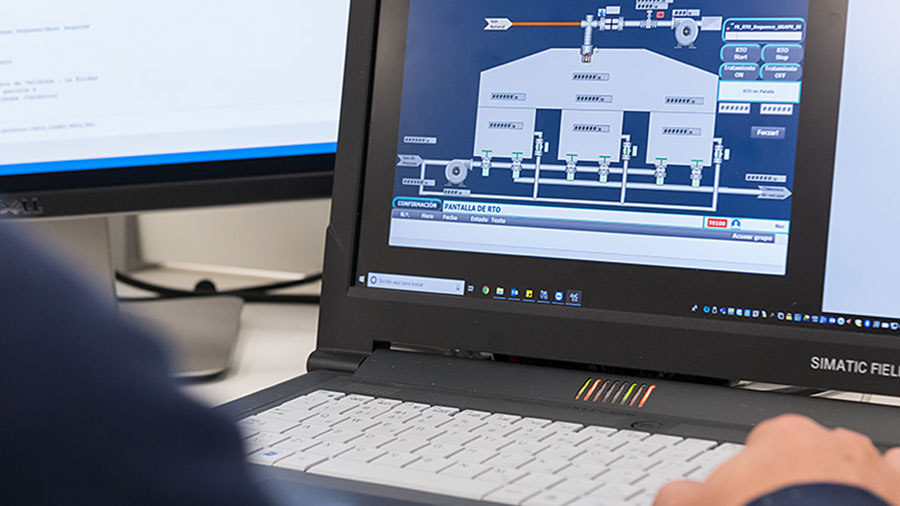


Tecam’s tailor-made design
You can always count on tailor-made solutions with Tecam and, where necessary, the development of specific components, software and/or materials. Our technicians engage with every project, using their
No matter how big or complex the problem, Tecam is the technology partner that will provide you with the solutions you need at all times.
Some of the key advantages
The advantages of installing an RCO system include the ability to efficiently eliminate VOCs at a lower temperature, thanks to the catalytic process.
The lower oxidation temperature translates to a lower consumption of natural gas.
RCO systems are typically used for flows with a low concentration of VOCs (< 0.5 g/Nm3). However, you must bear in mind that these VOCs should not contain heavy metals, sulphur compounds, silicon compounds or phosphorus compounds, as these could poison the catalyst.

Contact us
What is an RCO?
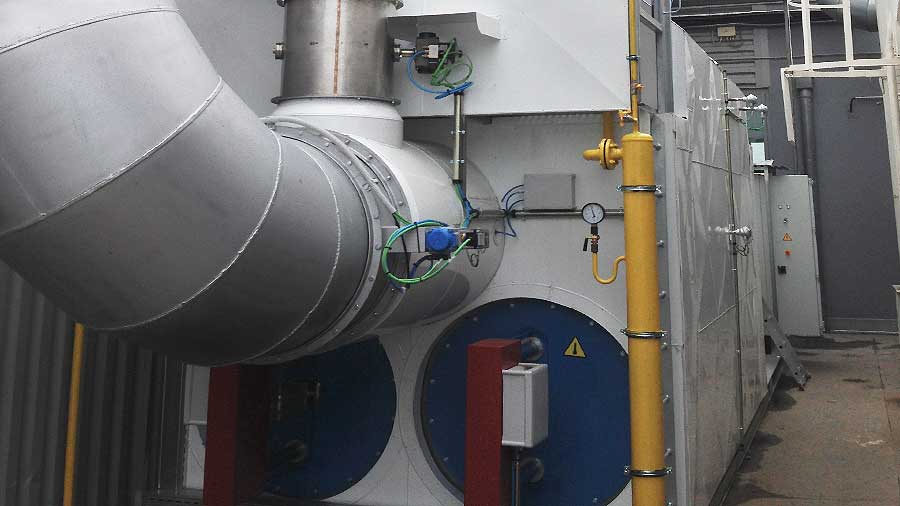
An RCO is a piece of equipment designed to eliminate Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs). It is formed of three towers with ceramic beds, where energy is recovered; a catalytic bed located in the upper part of each tower, which accelerates the oxidation reaction; and a combustion chamber where the temperature is kept constant in order to enable oxidation. The organic compounds it eliminates are mostly made up of carbon and hydrogen: consequently, when they react with oxygen they form carbon dioxide and water.
After passing through the second tower, the air – now free from pollutants – is sent up the flue. The third ceramic tower is used to recirculate the purged elements, as all of the air must be oxidised during the valve sequencing. The sequencing procedure is repeated periodically, every 45-90 seconds, in order to make sure each tower is operating in the same way.
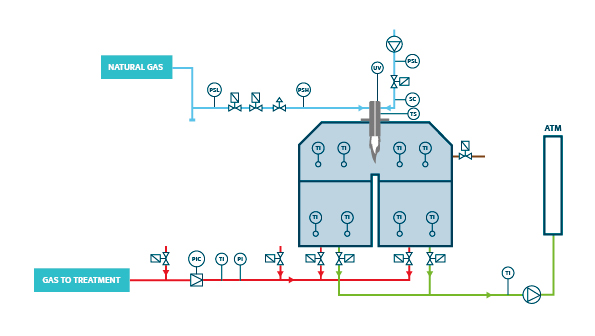
To minimise the consumption of fuel gas in the RCO, in the upper part of the ceramic towers there are catalytic beds that reduce the operating temperature of the combustion chamber, thereby ensuring full oxidation due to the action of the catalyst.
How an RCO works
A Regenerative Catalytic Oxidisation (RCO) system works as follows.
The contaminated air to be treated is sucked in by the main fan. The fan then pushes the air through the first ceramic tower. In this first tower, the air is heated. After the air has passed through the ceramic bed, it then reaches the catalytic bed, where the oxidation takes place at a temperature of 250 ºC – 450 ºC (depending on the organic compounds contained in the airflow). At the same time as air to be treated enters the first chamber, the now-oxidised air is passed through the second ceramic tower, in order to transfer its heat to the ceramic media. This cools the gas and heats the ceramic bed.
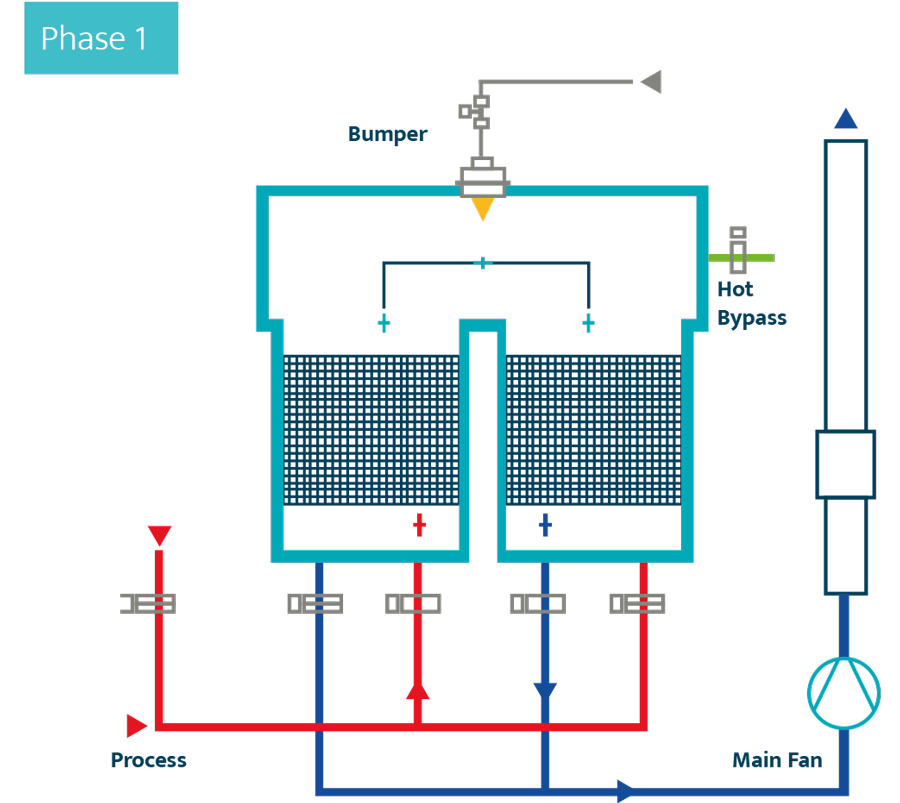
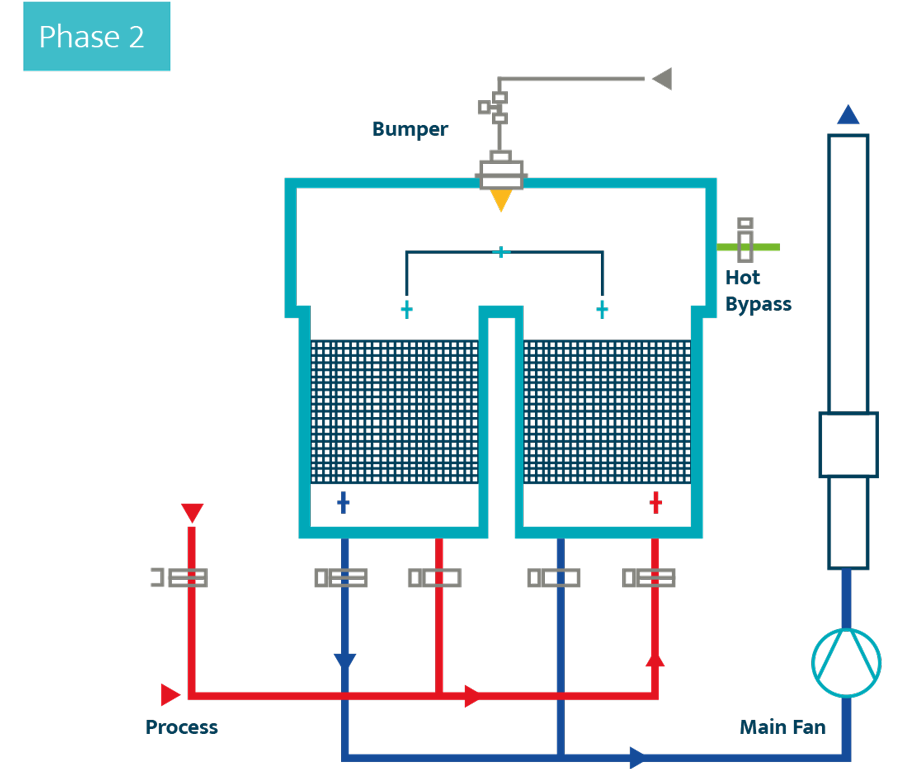
After passing through the second tower, the air – now free from pollutants – is sent up the flue. The third ceramic tower is used to recirculate the purged elements, as all of the air must be oxidised during the valve sequencing. The sequencing procedure is repeated periodically, every 45-90 seconds, in order to make sure each tower is operating in the same way.
Specialists in the sectors that are most sensitive to environmental impacts
We drive sustainable productivity and innovation for industries with more extensive and more complex needs.
Related news
How to Address the Challenges Faced by Environmental Managers in the Industrial Sector
How Tecam can help industrial companies’ environmental managers tackle challenges and turn environmental obligations into opportunities for improvement and leadership.
10 Current Challenges of Engineering Companies and How Tecam Can Provide Solutions
Collaboration between engineering companies and their specialized partners is vital to address complex environmental challenges in strategic sectors such as the pharmaceutical, chemical and petrochemical industries. Identifying a partner that can mitigate the critical...
Emissions Treatment in the Pharmaceutical Industry
The pharmaceutical industry faces significant challenges in managing its emissions due to the complexity of its production processes. At Tecam, with over 15 years of experience in the sector, we specialize in providing advanced technological solutions for...


















